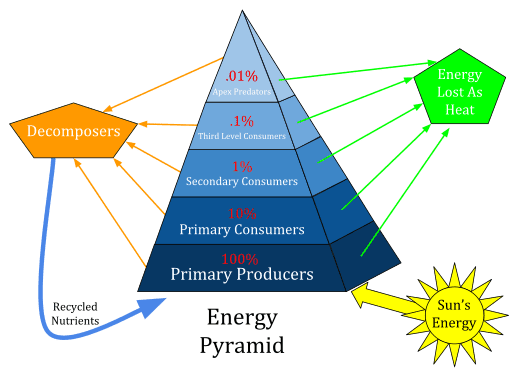
Energy Pyramid: Definition, Levels and Examples
Energy Pyramid is sometimes referred to as an ecological pyramid or trophic pyramid. It is a graphical representation between various organisms in an ecosystem. The pyramid is composed of several bars. Each bar has a different trophic level to represent. The order of these bars is based on who feeds on whom. It represents the…