What is a Comet and What are Various Parts of a Comet?
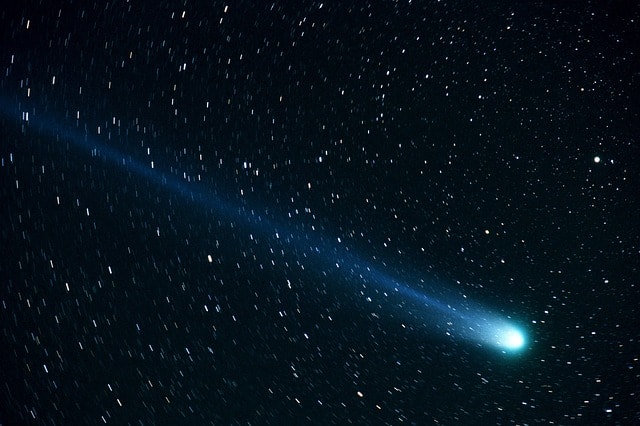

A Comet is a small, fragile and irregularly shaped body which is composed of a mixture of grains and frozen gases that are non-volatile. Comets always follow a long path around the Sun. Even on the telescope, most comets are not visible. They only become visible when they are close enough to the Sun. This is because; they are radiated by the sun to sublime the volatile gas hence blowing away the minute bit of this solid material. A comet is decidedly smaller in size as compared to the planets. They have a diameter that ranges between 2460 feet to 12 miles or less.
Most people refer to comets simply as small, city or mountain-sized rubble piles of volatile ices and rocks which occur in the solar system in infinite numbers. Comets are separated into three distinct parts called the tail, nucleus and the coma which ensures its workability. Comets work in the sense that they tend to be more explicit when they come closer to the source of illumination, the Sun. The tail of a comet is made up of three other parts, the ion tail, the hydrogen envelope, and the dust tail. All these are also vital for the movement of the comet both to and from the sun as indicated below.
Various Parts of a Comet
Three main components of a comet have been identified. The parts include the tail, the nucleus and the coma. The tail section of a comet is divided into three other parts. It has been observed that some comets tend to be broader than the distance between the earth and the sun when combined with the length of their tails. You should not forget that the distance that separates the sun and the earth is almost ninety-three million miles. Below is a description of the significant parts of a comet:
-
The Nucleus
The nucleus of a comet is made up of ice, gas, dust, and rocks. It is found right at the center of the head of a comet. The nucleus of a comet is often frozen. The part which is occupied by the gas in the comet’s nucleus is made up of carbon dioxide, the carbon monoxide, ammonia, and methane.
The comet’s area which is made up of the nucleus encompasses between 0.6 to around 6 miles. At times, it is even more than this distance. The nucleus, following this combination of materials, carries the most mass of the comet. The nucleus of a comet is also regarded as one of the darkest objects ever witnessed in the space.
-
The Coma
The coma as one of the significant parts of a comet is made up of, particularly gaseous materials. It encompasses the nucleus. It has a size of over 600000 miles across. Similar to the nucleus of the comet, the coma is also made up of ammonia, water vapor, carbon dioxide, natural gas, and dust.
The coma, together with the comet’s nucleus will form the head part of the comet. The coma is also known to be the part of the comet which is very visible. If the astronomers view a comet, they are likely to see this part and not the tail nor the nucleus.
-
The Tail
The tail of a come is the last part of a comet and is made up of three distinct parts. The tail will either guide or follow the coma and the nucleus of a comet. The primary tree parts of the tail are:
- Plasma or ion tail: the plasma or the ion tail as many would refer to it is made up of ions which are charged. The ions tend to consistently face away from the sun following the presence of the solar winds. As a result, this ion tail tends to follow a comet towards the sun or leads it away from the same source of heat. The ion tail, in most cases, is about 60 million miles in length.
- The dust tail: the dust tail of a comet is often seen to be very wide and long. It is composed of lots of microscopic particles of dust. The dust particles are often buffeted by the many protons which are emitted by the sun. The dust tail of a comet usually appears to be curved due to the high motion with which a comet moves. However, this part of the comet’s tail will fade as the comet moves further from the sun which is its main illuminator.
- The envelope tail: among the three tail parts of the comet, the envelope tail is made up of hydrogen gas. It is found just within the ion and the dust tail parts. The envelope tail comprises about 60 million miles in length and 6 million miles in the breath. Similar to the other tail parts of a comet, this tail appears larger enough when the comet is near the Sun.
How Do Comets Work?
Comets are believed to orbit around the sun in either Kuiper belt or Oort cloud. In case another star comes closer or passes by the solar system, the Oort cloud, and the Kuiper belt is pushed away by the gravity of the star. This makes the comet to move towards the direction of the sun in a very elliptical orbit.
At this time, the sun lies at a single focus of the ellipse. Comets typically have a shorter orbit period which is not more than 200 years; one example of a comet that orbits around the sun for a lesser period than 200 years include the Halley’s Comet. However, some comets such as the comet hale bop will orbit the Sun for more extended periods that are more than 200 years.
As the comet is passing with 6 AUs (astronomical unit) of the primary star, the sun, the ice that is contained in its nucleus begins to converts directly to gas from solid. This process is known as sublimation. It is also the process by which fogs are formed. Upon the sublimation of the ice, the dust and gas particles flow away from the sun hence forming the tail of the comet.
As it approaches the sun, a comet warms up, and several other parts begin to appear. At this time, one can observe the nucleus, the coma, the dust tail, the hydrogen envelop as well as the ion tail. As they pass through the solar system, comets are often broken into smaller pieces by the gravity of Jupiter. The most significant impact that has been recorded in the history of comets is the comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 which was split into 20 pieces. The pieces all collided with planet Jupiter.
The comets are known to sprout larger tails and comas when they approach the sun. During such times, they tend not to be on fire. However, they melt and disintegrate as they exhibit a couple of tail structures. Most comets possess orbits which are very eccentric that makes it dive into the inner parts of the solar system. The diving occurs from the lots of dozens of the distance of AU at odd inclinations to help it come within a few kilometers next to the surface of the Sun.
Sources:
http://www.qrg.northwestern.edu/projects/vss/docs/space-environment/1-what-is-a-comet.html
http://cse.ssl.berkeley.edu/SegwayEd/lessons/findplanets/find_comet/WhatsAcomet.html