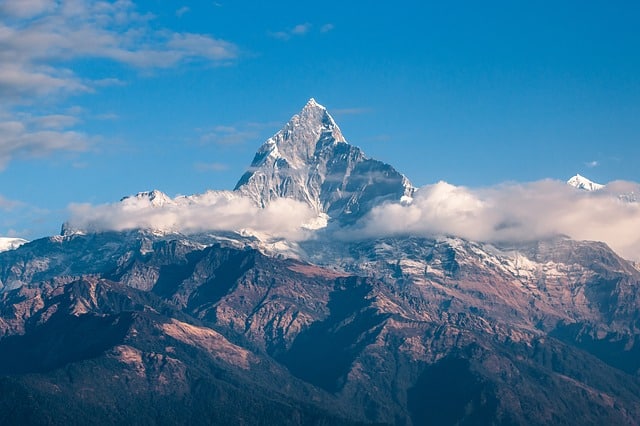
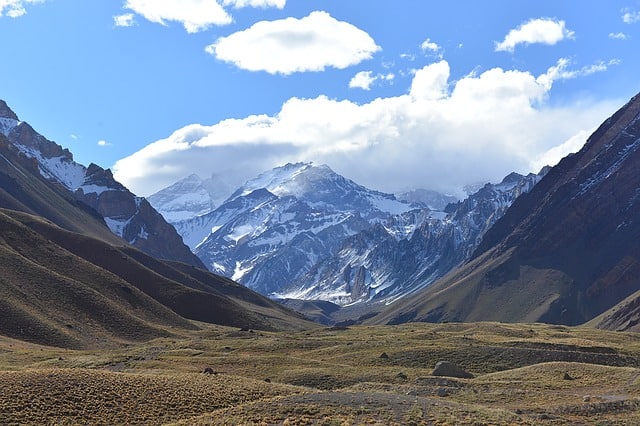
Himalayan Mountain: Range, Location and Interesting Facts
The Himalayan mountain is a collection of mountains in Asia, sometimes referred to as the ‘Himalayas’ or ‘the abode of Snow’ in Sanskrit. These mountains form a huge range of mountains which surround the western and southern edges of the Tibetan plateau. Himalayan Mountains separate the plains of the Indian subcontinent from those of the…